- Home
- Blog
- Medical Dermatology
- The facts about Molluscum Contagiosum
The facts about Molluscum Contagiosum
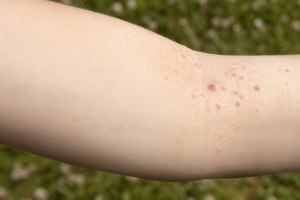 Molluscum Contagiosum is a common skin disease caused by a pox virus. This virus is easily spread from person to person by skin contact or by sharing towels or clothing. Skincare Physicians’ Dr. Tania Phillips shares the basics about this common skin disease.
Molluscum Contagiosum is a common skin disease caused by a pox virus. This virus is easily spread from person to person by skin contact or by sharing towels or clothing. Skincare Physicians’ Dr. Tania Phillips shares the basics about this common skin disease.
What does Molluscum Contagiosum look like?
Molluscum Contagiosum usually appears as tiny skin colored tiny bumps which can range in number from 1 – 2 to 10 – 20 bumps. Molluscum is usually painless; occasionally it can be itchy. Molluscum can appear anywhere on the body. It is commonly seen on the arms, legs and trunk.
Is Molluscum contagious?
Molluscum is contagious when the bumps are still present. Once the bumps go away, the patient is no longer contagious. Patients, however, may continue to get new bumps.
How to treat Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum will often go away on its own. Without treatment, they usually can clear completely within 2 – 4 months. It can be treated with a variety of methods. Dermatologists often treat with a very cold spray, called liquid nitrogen. The bumps can also be treated with Curettage, using a small tool that can be used to scrape the bumps off the skin.
Other treatments include topical products, such as cantharidin or trichloroacetic acid which can be applied to the bumps. This will make them blister and then go away.
Do’s and Don’ts
If you think you have molluscum, see a dermatologist to get an accurate diagnosis. Try not to pick or scratch at the bumps as this may spread the condition. Do not come into close contact with others as you may spread the virus. Do not share your razor and towels. Do not wash cloth or other items with other people.
Additional questions or concerns about Molluscum Contagiosum? Contact our dermatologists at SkinCare Physicians near Boston.



Leave a Reply